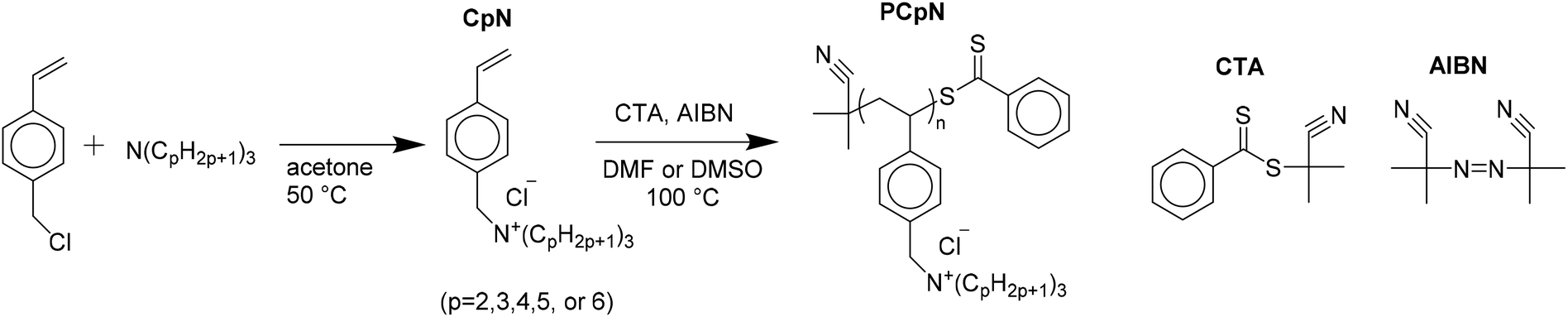
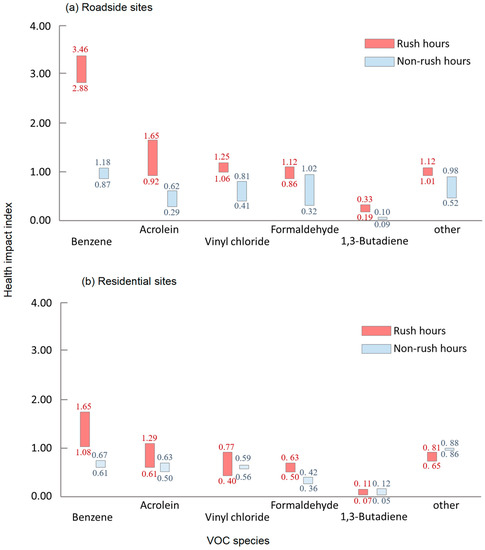
Why Vinyl Chloride Is Less Reactive Than Ethyl Chloride
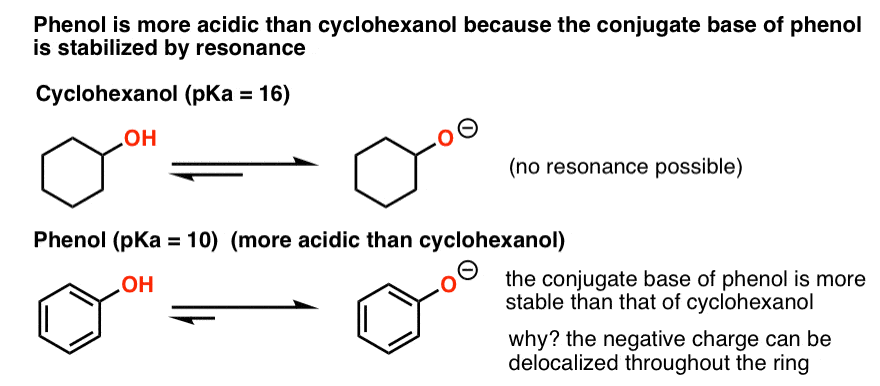
Allyl chloride is more reactive than vinyl chloride because in vinyl chloride lone pair of chlorine are in resonance so chlorine will not get removed easily while in case of allyl chloride resonance is not present.
Why vinyl chloride is less reactive than ethyl chloride. Cl can more easily attract the bonded electrons from sp3 carbon and therefore is more reactive. Ncert ncert exemplar ncert fingertips errorless vol 1 errorless vol 2. In case of ethyl chloride there is only single bond then it is easier to break then vinyl chloride is less reactive then ethyl chloride. As sp2 hybridized carbon is more electronegative then sp3 hybridized.
There s no such resonance in propylchloride. Ncert p bahadur iit jee previous year narendra awasthi ms chauhan. Ch3 ch2 is more stable. In vinyl chloride cl is linked with sp2 hybridized carbon whereas in allyl chloride cl is linked with the sp3 hybridized carbon as sp2 hybridized carbon is more electronegative then sp3 hybridized cl can more easily attract the bonded electrons from sp3 carbon and therefore is more reactive.
Why is chlopropyl chloride less reactive than cyclopentyl chloride towards s n 1 reaction. Therefore vinyl chloride less reactive than ethyl chloride. Hence chlorine reacts readily. Vinyl chloride is the chloride which is attached to the double bonded carbon so it forms resonace and gets partical double bond and get higest ionization enthalpy where as the ethyl chrolide doesnot have the property of resonance.
On the other hand in ethyl chloride carbon chlorine bond is a single bond only. As a result there is partial double bond character in the c cl and its bonds strength increases. In vinyl chloride h 2 c hc cl the electron pair on the chlorine atom conjugates with the pi electron pairs of the double bond. Answered by ramandeep 2nd jan 2020 01 27.
Vinyl chloride is less reactive than ethyl chloride towards towards nucleophyllic substituiton because of double bond character and sp2 hybridisation in case of vinyl chloride which results in strengthening of bond and hence nucleophile s attack cannot result in substituiton. Consequently it becomes difficult to cleave c cl bond as compared to the ethyl chloride where no such conjugation is possible.